Research in Kikuchi Lab.
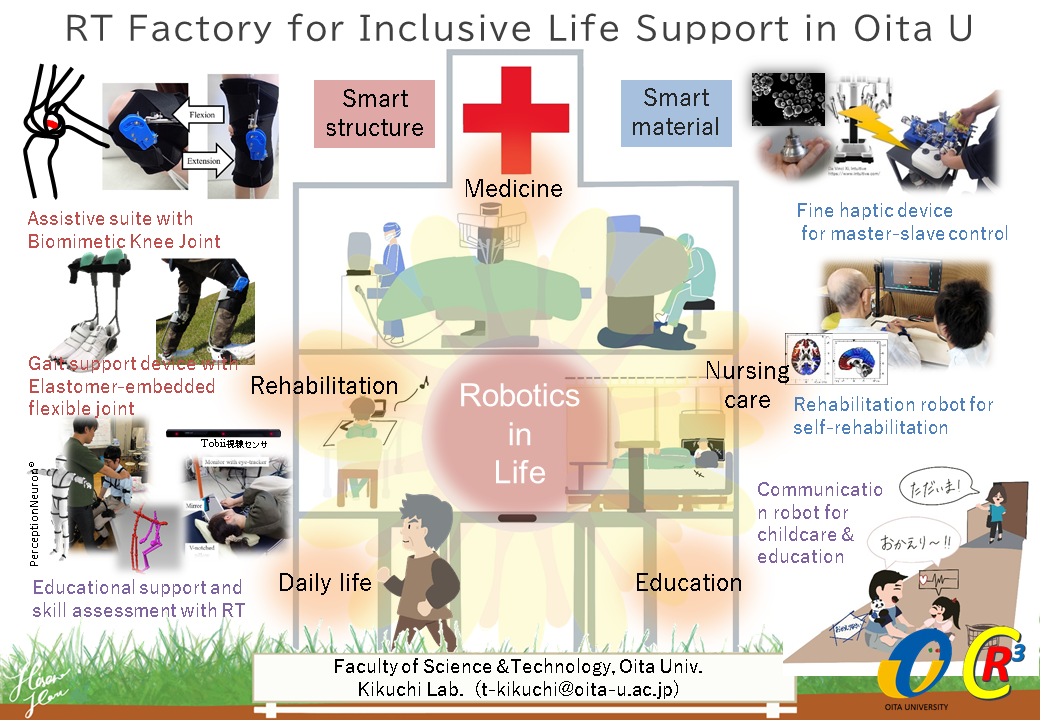
Category A:
Smart Material Robotics- A1: Mechatronics Devices Using Functional Materials
- A2: MRF Actuator with Multi-layered Disc MR Clutches for Haptics
- A3: Rehabilitation robot for upper limb training, D-SEMUL
- A4: Intelligently Controllable Ankle-Foot Orthosis, i-AFO
- A5: Intelligently Controllable Walking Aid, i-Walker
- A6: VR Cycling with Cylindrical MR Fluid Brake
- A7: VR Walking with MRE Haptic Interface
Category B:
Smart Structure Robotics- B1: AFO with Elastomer Embedded Flexible Joint, EEFJ-AFO
- B2: Shoes with EEFJ, EEFJ-Shoes
- B3: Power asssit suit with Biomimetic Knee Joint, Active BKJ
- B4: Knee orthosis with BKJ, Passive BKJ
- B5: Intelligently Seating System, i-Seating
Category C:
Educational support and skill assessment with RT- C1: Gaze Measurement Method Using Cheap Eye Tracker & Mirror Reflection
- C2: Motion Analysis for Optimization of Transfer Motion in Nursing Care
- C3: Leg-Shaped Haptic Simulator (Virtual Patient: Leg-Robot)
- C4: Automated Treadmill and Gait Analysis
Category A:
|
|
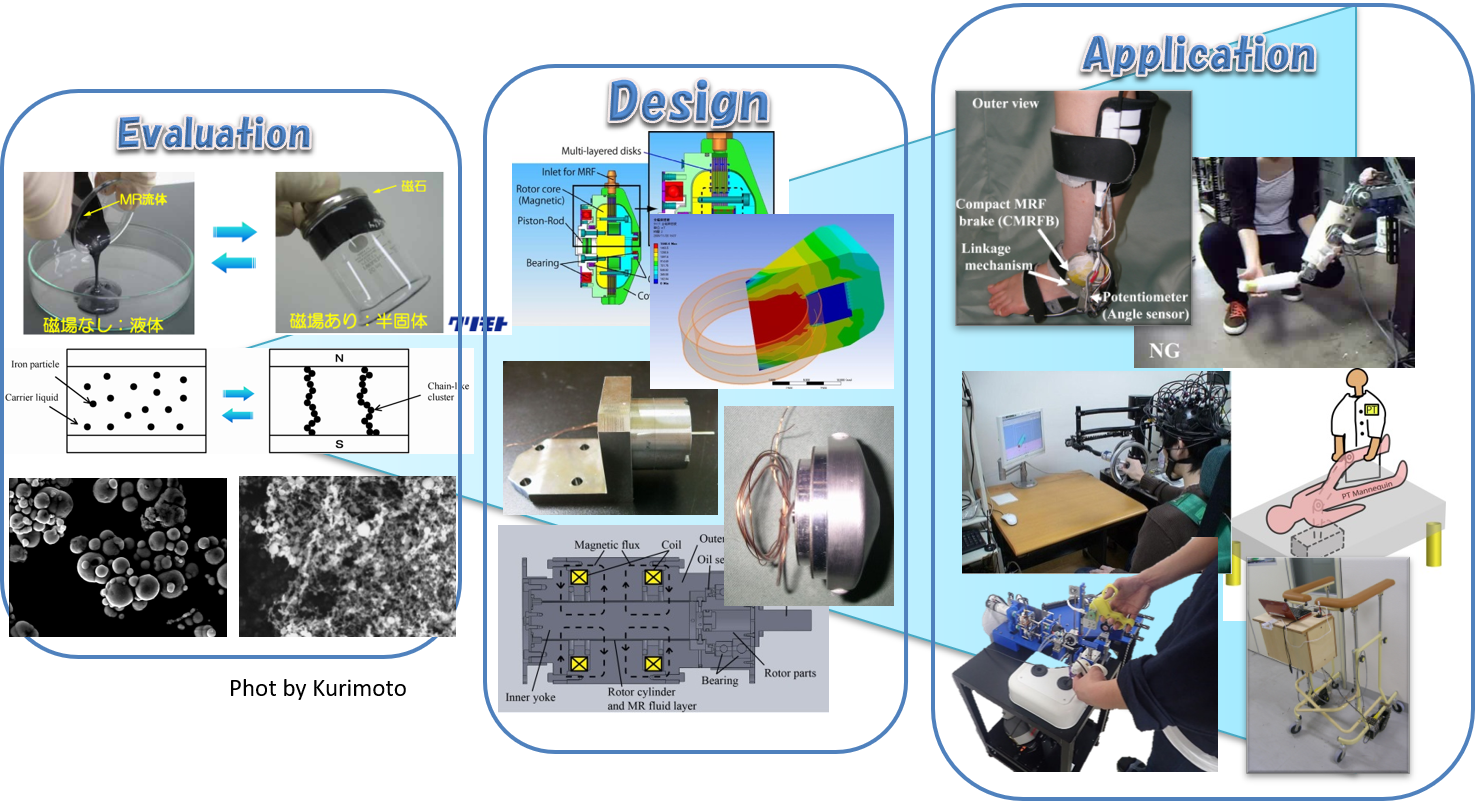
(A1) Mechatronics Devices Using Functional MaterialsThere is a strong demand for a human-machine-coexistent machine, e.g. a power-assist system or a computer-aided rehabilitation system, in the context of the super-aging society. In such a human-machine-coexistent system, it is important to guarantee hardware-level safety by utilizing human-friendly actuators. In this study, we have developed several types of clutch/brake devices for such human-friendly actuators or robot systems by using functional fluids (Electro-Rheological Fluid, Magneto-Rheological Fluid, and Magnetic Field Sensitive Elastomer). |
|
(A2) MRF Actuator with Multi-layered Disc MR Clutches for HapticsMagnetorheological fluids (MRFs) are composite materials made of ferromagnetic particles, medium oils, and several types of additives. We have developed actuation systems for the fine haptic control of master-slave robots. In this study, we proposed a new structure of an MRF-based actuator suitable for haptic devices. |
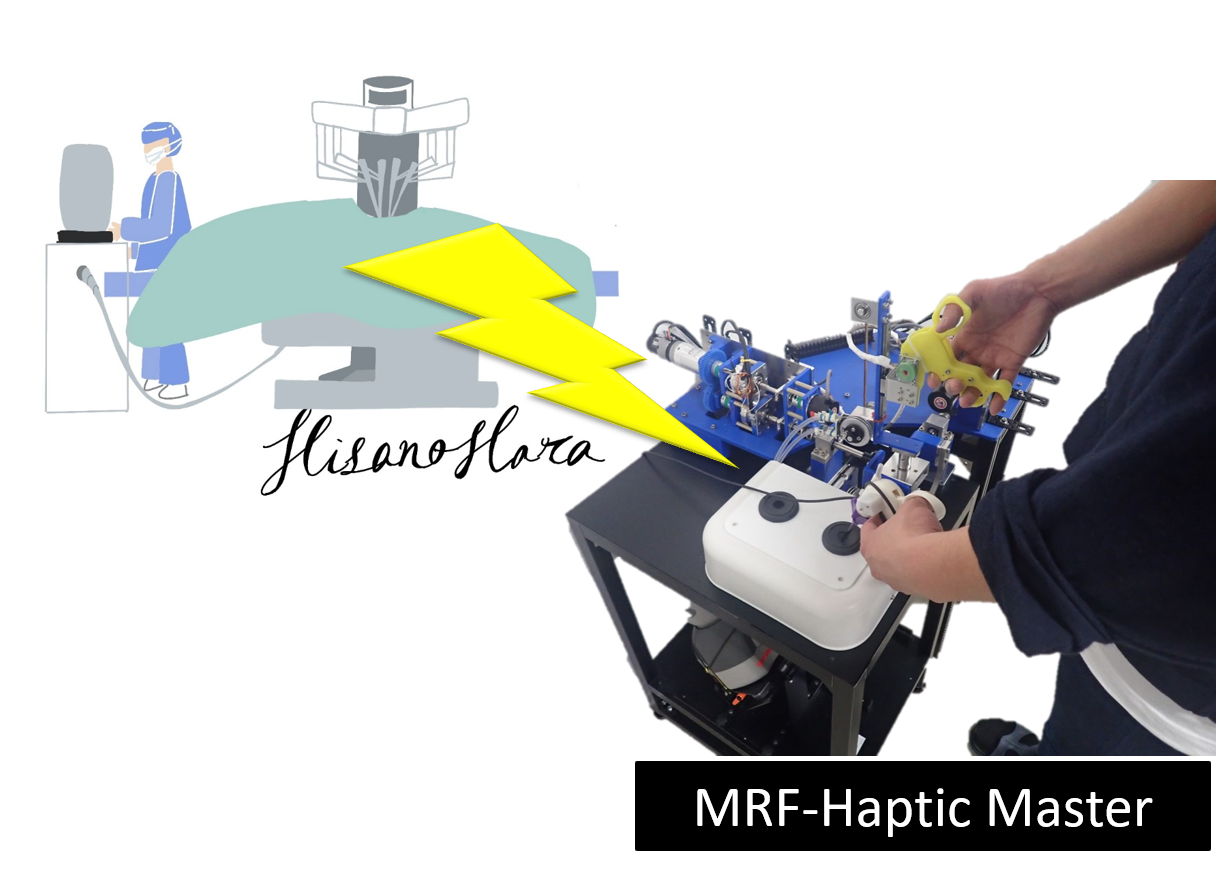
|
(A3) Rehabilitation robot for upper limb training, D-SEMULTo establish evidence-based therapy for motor rehabilitation of the upper limbs, we developed a desktop simple exercise machine for upper limbs (D-SEMUL) as a low-cost and high-quality rehabilitation robot. |
|
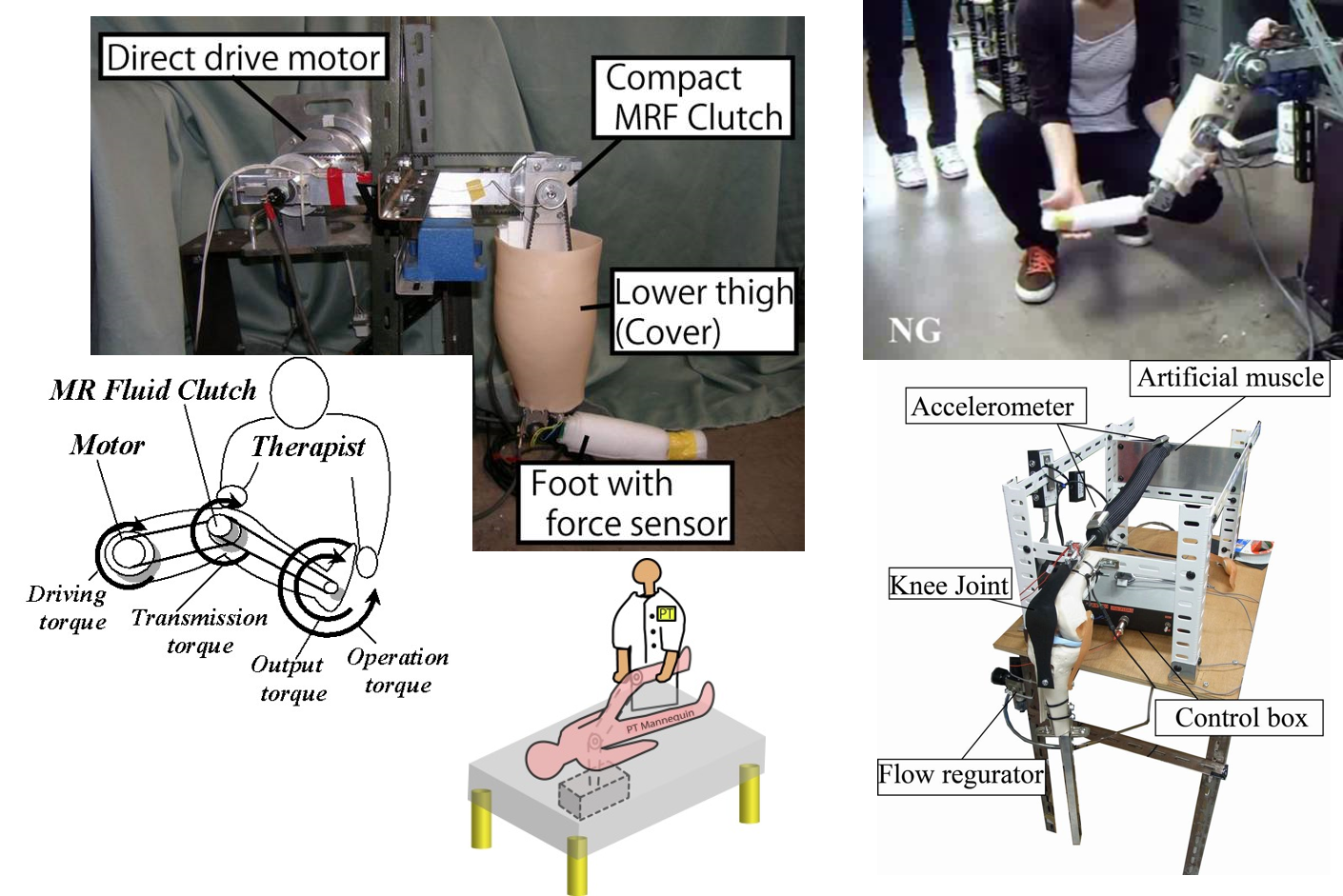
(A4) Intelligently Controllable Ankle-Foot Orthosis, i-AFOAnkle-foot orthoses (AFOs) are orthotic devices that support the movement of the ankles of disabled people, for example, those suffering from hemiplegia or peroneal nerve palsy. We have developed an intelligently controllable AFO (i-AFO) in which the ankle torque is controlled by a compact magnetorheological fluid brake. Gait-control tests with the i-AFO were performed for a patient with flaccid paralysis of the ankles, who has difficulty in voluntary movement of the peripheral part of the inferior limb, and physical limitations on his ankles. By using the i-AFO, his gait control was improved by prevention of drop foot in the swing phase and by forward promotion in the stance phase. |
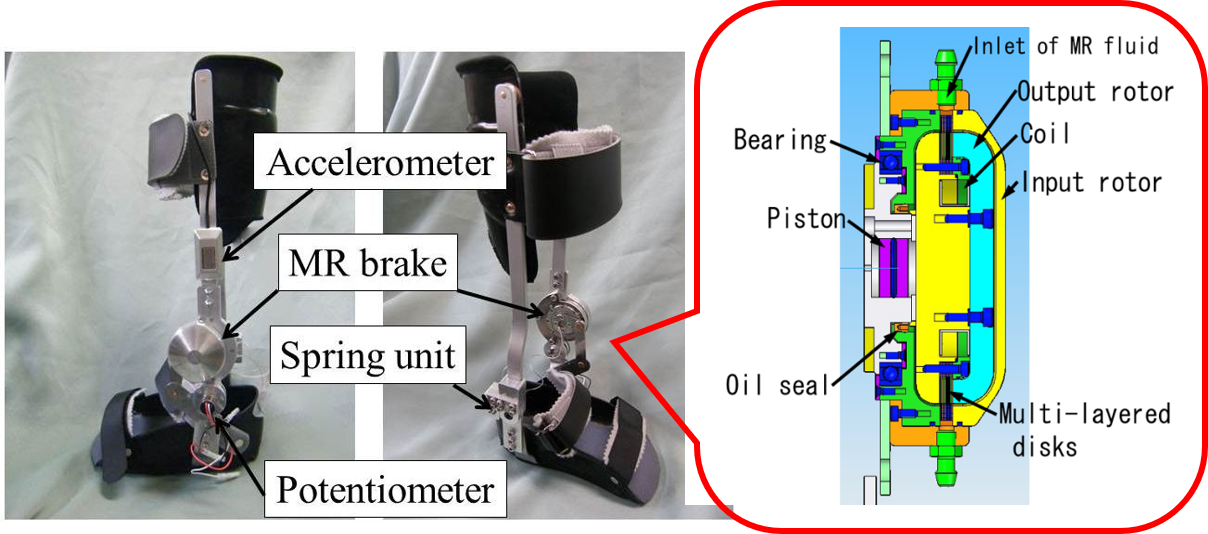
|
(A5) Intelligently Controllable Walking Aid, i-WalkerCaster walkers are kinds of walking aids which consist of supporting frames, casters, and wheels. These are regularly utilized as walking aids in hospitals, nursing homes and individual residences. Their casters and wheels allow them to easily move to desired places. However falling accidents often happen when these move without users. In another case, it is hard to move to desired directions if users have imbalance in their motor / sensory function. To improve safeness and operability of walkers, we installed MR fluid brakes on the wheels of a walker and controlled its walking speed and direction. We named i-Walker to this intelligently controllable walker. |
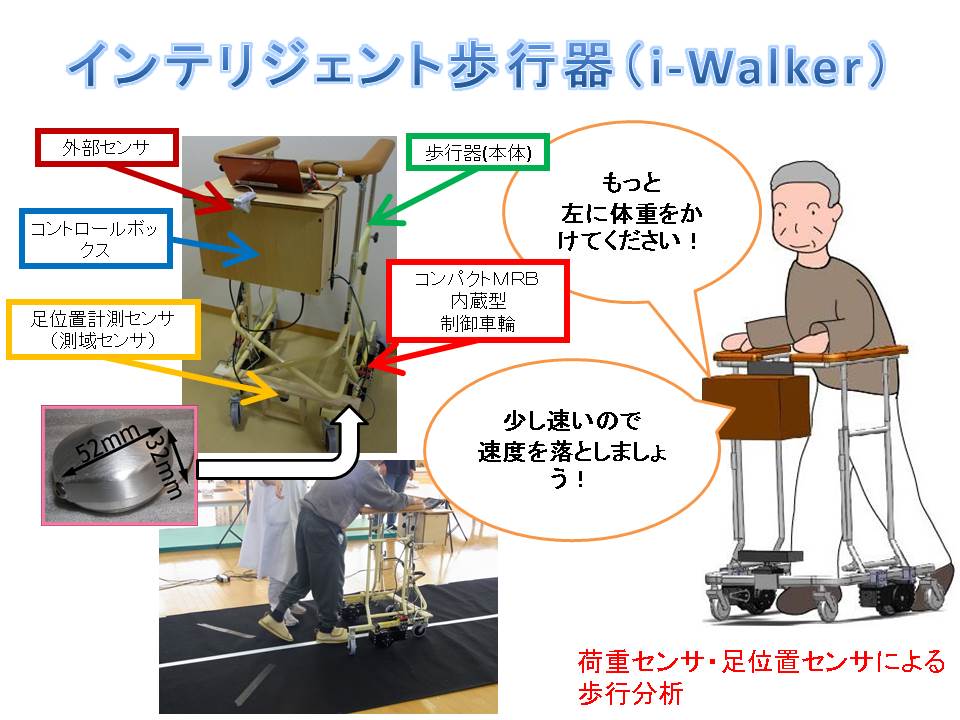
|
(A6) VR Cycling with Cylindrical MR Fluid BrakeDementia is one of the major concerns for aging populations. There is a great deal of evidence that aerobic exercises positively affect older patients with dementia. Our goal is to develop a virtual cycling system (Fig) that can control a wide range of force feedback from its pedals and provide safe cycling experiences for the elderly, to prevent dementia. We developed an MRB with a rotational cylinder to control the force of the virtual cycling system. We proposed a structure with a rotor cylinder and multiple coils to produce a wide range of magnetic flux densities on the surface of the cylinder and create an effective MR effect. Currently, we are developing a virtual cycling system by attaching a cylindrical MRB and controlling pedal force according to virtual world situations presented on a screen. |

|
(A7) VR Walking with Haptic InterfaceMagnetic-field sensitive elastomers (MSEs) are compounds formed of magnetic materials and non-magnetic elastomers. The viscoelasticity of the MSE can be adjusted with an external magnetic field. The MSE used in this study is a composite of polymer solids and magnetic particles (Mitsumata, T., & Ohori, S. (2011). Megnetic plyurethane elastomers with wide range modulation of elasticity. Polymer Chemistry, 2, 1063-1067). We are currently engineering a haptic interface using the MSE. The final goal of this study is to develop a virtual walking system (Fig) that enables users to feel sensation on the soles of their feet on a variety of ground types. |

|
Category B:
|
|
(B1) AFO with Elastomer Embedded Flexible Joint, EEFJ-AFOWalking is one of the most important functions in daily living, and difficulty in walking represents a significant barrier . Therefore, gait training is a high priority in rehabilitation medicine. Due to muscle weakness, stumbles in swing phases and slapping foot at initial contact of gait increase in elderly individuals. Walking supports such as ankle foot orthoses (AFOs) are available. In our previous study, we proposed a basic structure of an elastomer-embedded flexible joint (EEFJ) and developed an ankle support. According to the experimental results, our AFO with the EEFJ (EEFJ-AFO) reduced the burden on the tibialis anterior muscle in swing phases. In addition, it reduced the ankle angle only during the pre-swing phase. |

|
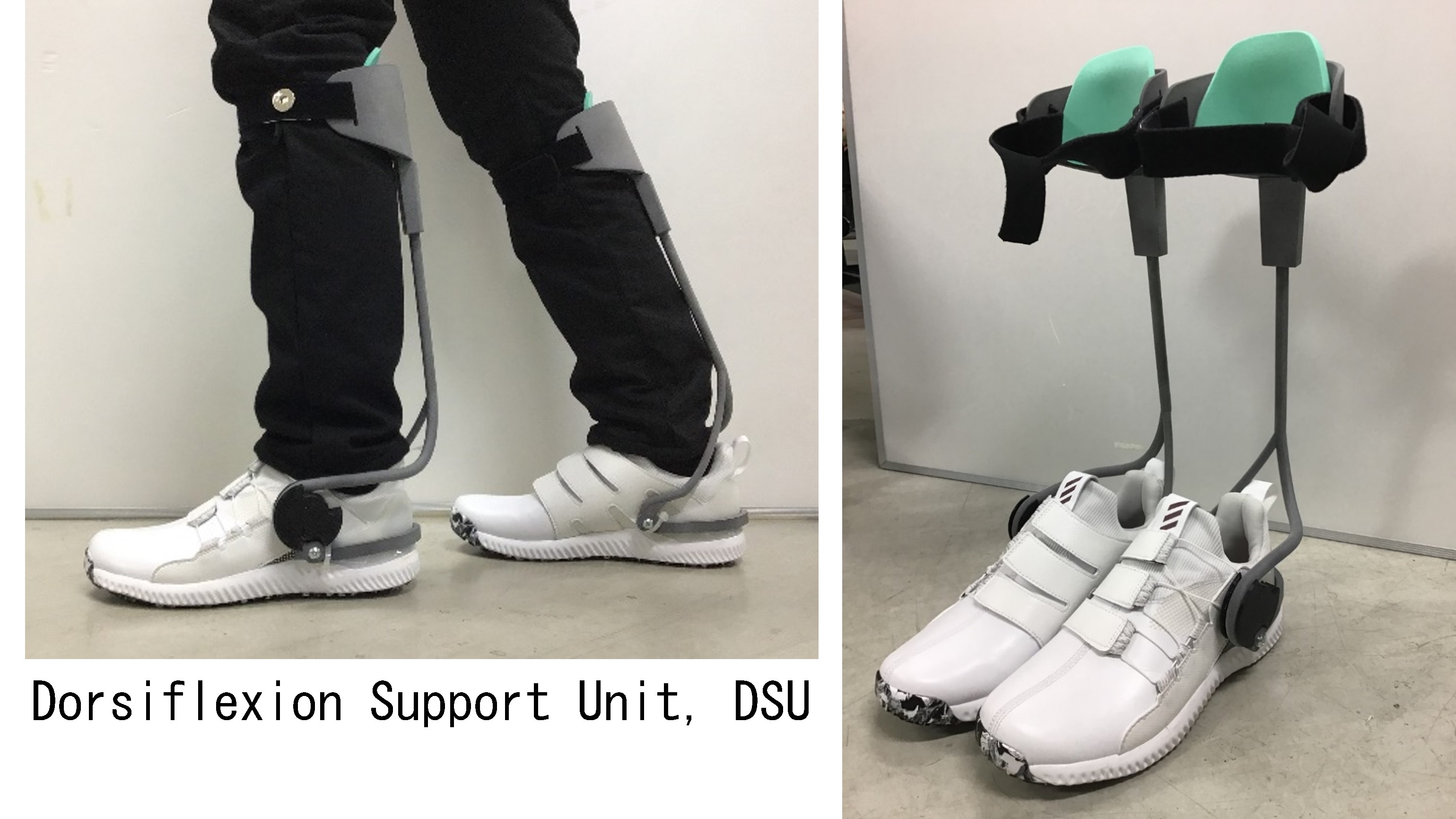
(B2) Shoes with EEFJ, EEFJ-ShoesWe believe that the function of the EEFJ is also useful in the walking support for elderly individuals with frailty in ankle motions and functions. However, AFOs are not suitable for such uses. Therefore, in our new study, we have decided to develop burden-reducing shoes by using the EEFJ (EEFJ-shoes) for elderly individuals with the frailty. |

|
(B3) Power asssit suit with Biomimetic Knee Joint, Active BKJMovement of the knee joint of a human includes rolling and sliding. There also exist rotations in the frontal and horizontal planes. To assist the standing movement of a human, we developed a bio-inspired knee joint and torque adjustment mechanism. We evaluated the motion, torque characteristics, and stress of the developed mechanism. |
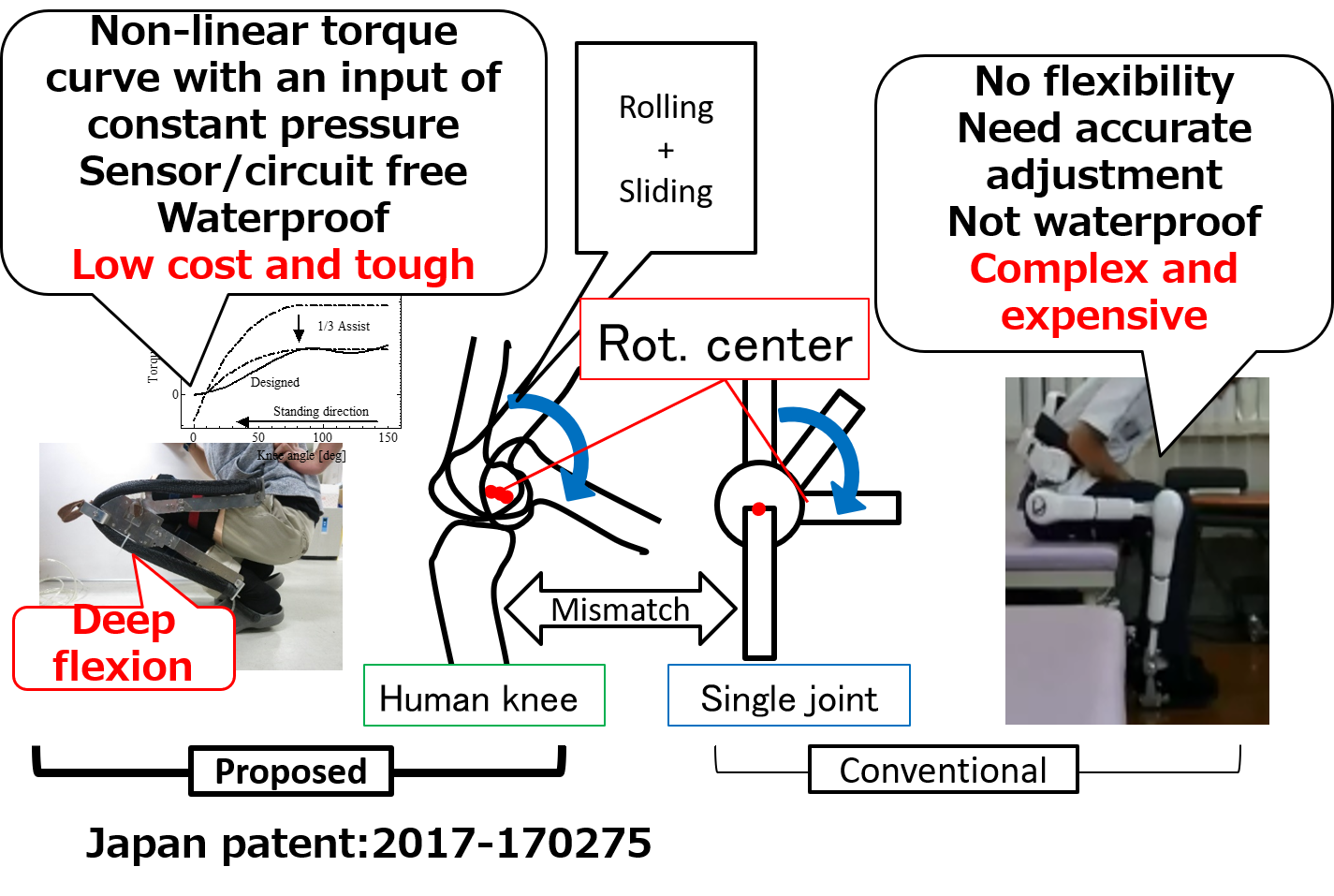
|
(B4) Knee orthosis with BKJ, Passive BKJWe have developed a passive-type biomimetic knee joint (BKJ) for stand-up motions for the labor and elderly. To evaluate shear stresses and strains between the mechanical parts of the devices and users’ skins, shear-force sensitive sheets (SSS) and electromyograms (EMG) were applied. |
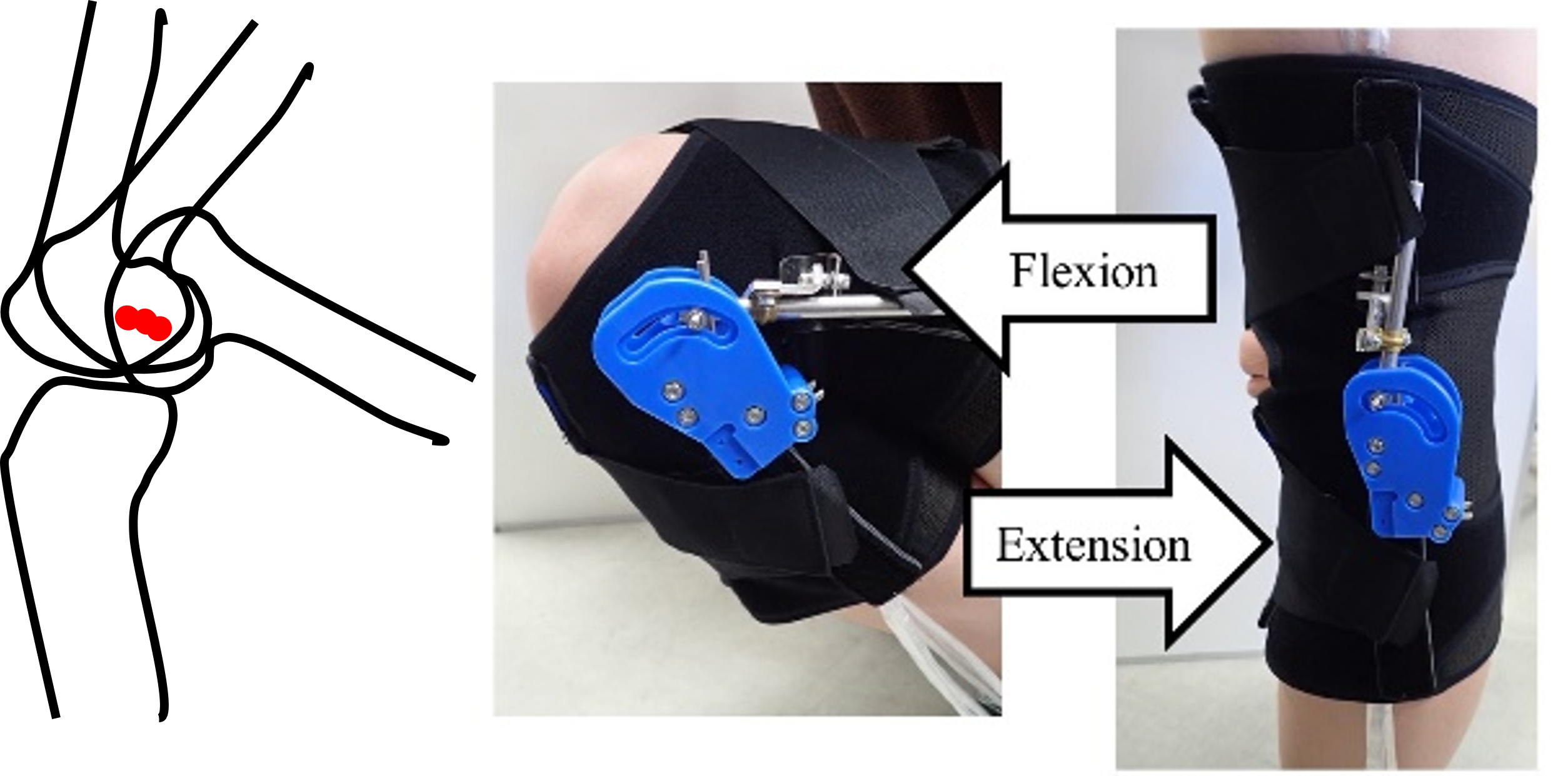
|
(B5) Inteligently Seating System, i-SeatingA proper seating is very important for severe cerebral palsy patients, and has good influence on patients’ physical bodies and mentalities. Deformity of spine causes gaps between a back of patient and a wheel chair backrest. Generally, urethane cushions are used to fill up the gaps. However, this method cannot handle the deformation of posture of users. The objective of this study is to develop an automatically transformable seating system with air pressure. |

|
Category C:
|
|
(C1) Gaze Measurement Method Using Cheap Eye Tracker & Mirror ReflectionWe have developed eye-tracking systems to improve QOL of severely disabled children who spends many time on their bed. Cheap eye-tracking devices generally require 500-800 mm distance in the front of a user. However, many of the children lie in lateral position due to body deformation, and it is difficult to keep such large distance beside their beds. Therefore, we proposed a new eye-tacking method using a cheap eye-tracker with a mirror reflection. In this paper, we discussed a mathematical model for the mirror reflection method and designed the alignment of the user, mirror, and monitor with a sensor. In addition, we expanded this method for the projection on the wall. |
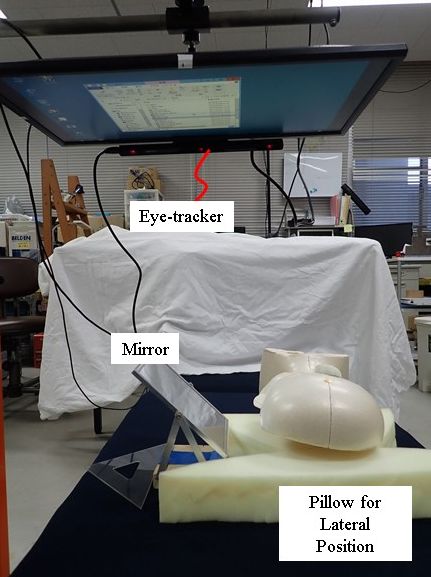
|
(C2) Motion Analysis for Optimization of Transfer Motion in Nursing CareIn this study we are trying to establish an educational model for the care-giver that can suggest the optimal care motion considering mechanical characteristics of both care-givers and patient. We have developed a motion analysis system and software as the educational tool for care-givers. This system composed of two sets of wearable motion capture sensor with many inertial measurement units (IMU). |

|
(C3) Leg-Shaped Haptic Simulator (Virtual Patient: Leg-Robot)In this study, we propose a leg-shaped robot (Leg-Robot) with a Compact MR Fluid Clutch (CMRFC) to demonstrate several kinds of haptic control of abnormal movements of brain-injured patients. This system can be used in practical trainings for trainees of physical therapies. |
|
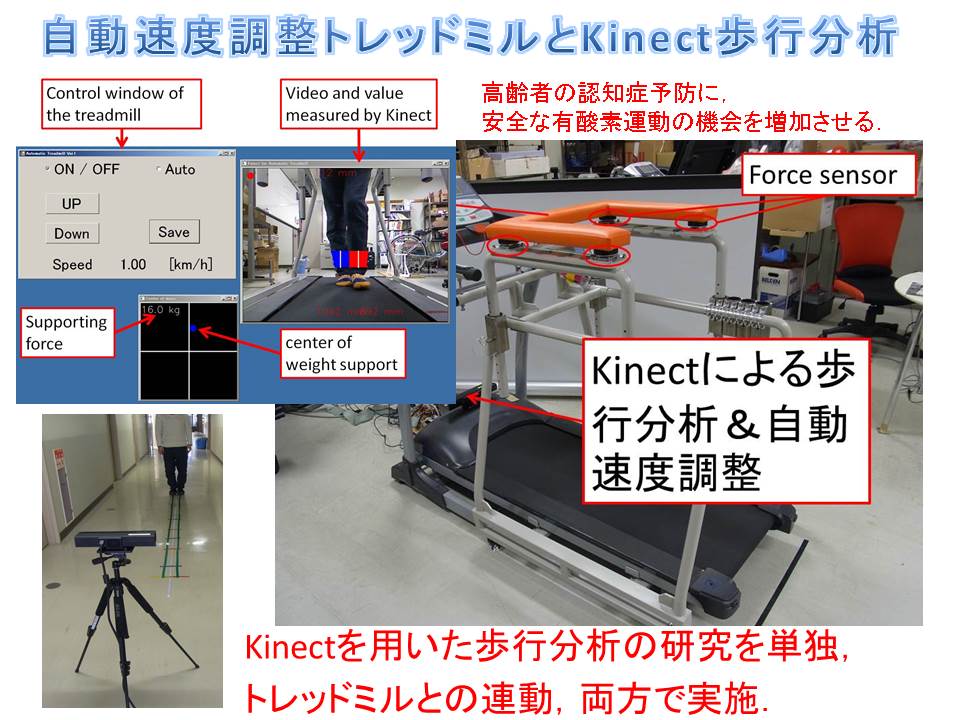
(C4) Automated treadmill and gait analysisxxx |
|


